What are the Different Stages of Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
+919999461292
MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

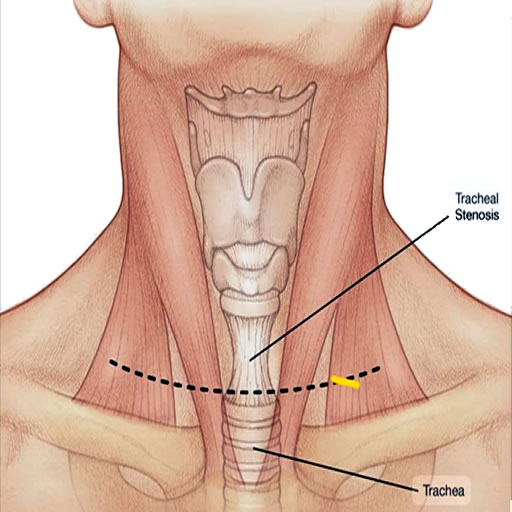
Tracheal stenosis is a condition characterized by a narrowing of the trachea, which can lead to severe breathing difficulty, coughing, and recurrent respiratory infections. It’s often a complication arising from prolonged intubation, tracheostomy, or can be due to inflammatory diseases such as tuberculosis and trauma, or tumors. Patients with tracheal stenosis typically report a progressive worsening of breathlessness, especially during exertion, and a high-pitched wheezing (stridor), signalling the need for medical evaluation.
Diagnosis involves bronchoscopic examination of the airways, pulmonary function tests, and imaging studies like CT scans to determine the stenosis’ severity and location. This stenosis can be “simple” or “complex”. “Simple stenoses” can be managed with bronchoscopic techniques (balloon tracheoplasty). or stent placement), however, “Complex stenosis” requires surgical intervention for long-term resolution, if bronchoscopic treatment (balloon tracheoplasty or stent placement) fails. Surgery typically involves removal the narrowed section of the trachea and reconstruct the airway (surgical resection and anastomosis).
Dr. Mohan Venkatesh Pulle, as an experienced tracheal (airway) surgeon, offers specialized treatment for tracheal stenosis, employing advanced techniques to optimize patient recovery and ensure the restoration of normal breathing.
See, Tracheal Stenosis is basically narrowing of your windpipe. Think of it like water pipe becoming narrow at some point. This makes breathing difficult because less air can pass through.
Most common causes are prolonged intubation, previous throat infection, or injury. Sometimes it happens after tracheostomy also. In your case, [specific cause] seems to be main reason.
It can be serious if left untreated, but nowadays we have very good treatment options. Key is early diagnosis and proper treatment. Don’t worry too much – we’ll handle this properly.
We have several options – endoscopic dilation, laser treatment, or surgery depending on severity. In your case, I’m thinking [specific treatment] might work best. We’ll discuss pros and cons in detail.
Not everyone needs surgery. We first evaluate severity and length of narrowing. Sometimes simpler procedures work well. But if surgery is needed, we use advanced minimally invasive techniques.
Recovery timeline varies. After endoscopic procedure, you might go home next day. For surgery, usually 5-7 days in hospital. Full recovery takes 4-6 weeks. But breathing improvement you’ll notice quite quickly.
There might be temporary voice changes, but usually returns to normal. We take special care to protect voice box during treatment. If needed, we’ll arrange speech therapy.
There’s small chance of recurrence, but we’ll teach you exercises and give medications to prevent this. Regular follow-up helps catch any problems early.
Main things – no smoking absolutely, avoid dusty environments, do breathing exercises regularly, complete all medicines. Also, very important to come for follow-up appointments.
Not everyone needs surgery. We first evaluate severity and length of narrowing. Sometimes simpler procedures work well. But if surgery is needed, we use advanced minimally invasive techniques.
Start with gentle walking first week after discharge. Then gradually increase as comfortable. No heavy exercise for 6 weeks. Swimming is excellent once wound heals completely.
You’ll notice breathing becomes easier, less noisy. Exercise capacity will improve. We’ll do regular breathing tests to measure improvement objectively.
Watch for increased breathing difficulty, noisy breathing, fever, or throat pain. If any of these occur, contact us immediately. But don’t panic – complications are rare.
Initially yes, but usually temporary. Main medicines are for preventing inflammation and infection. Some patients might need inhalers for few months.
Follow-up regularly, complete all treatments, do breathing exercises, maintain good throat hygiene. If you get throat infections, treat them properly and timely.
Important Note: “Remember, every patient’s condition is bit different. We’ll customize treatment plan for you. My team and I are always available if you have concerns. Good communication helps in better recovery.”
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable and often challenging disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a challenging and potentially life-threatening condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. When esophageal...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable adversary that can silently develop within the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube responsible for...
WhatsApp us