What are the Different Stages of Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
+919999461292
MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

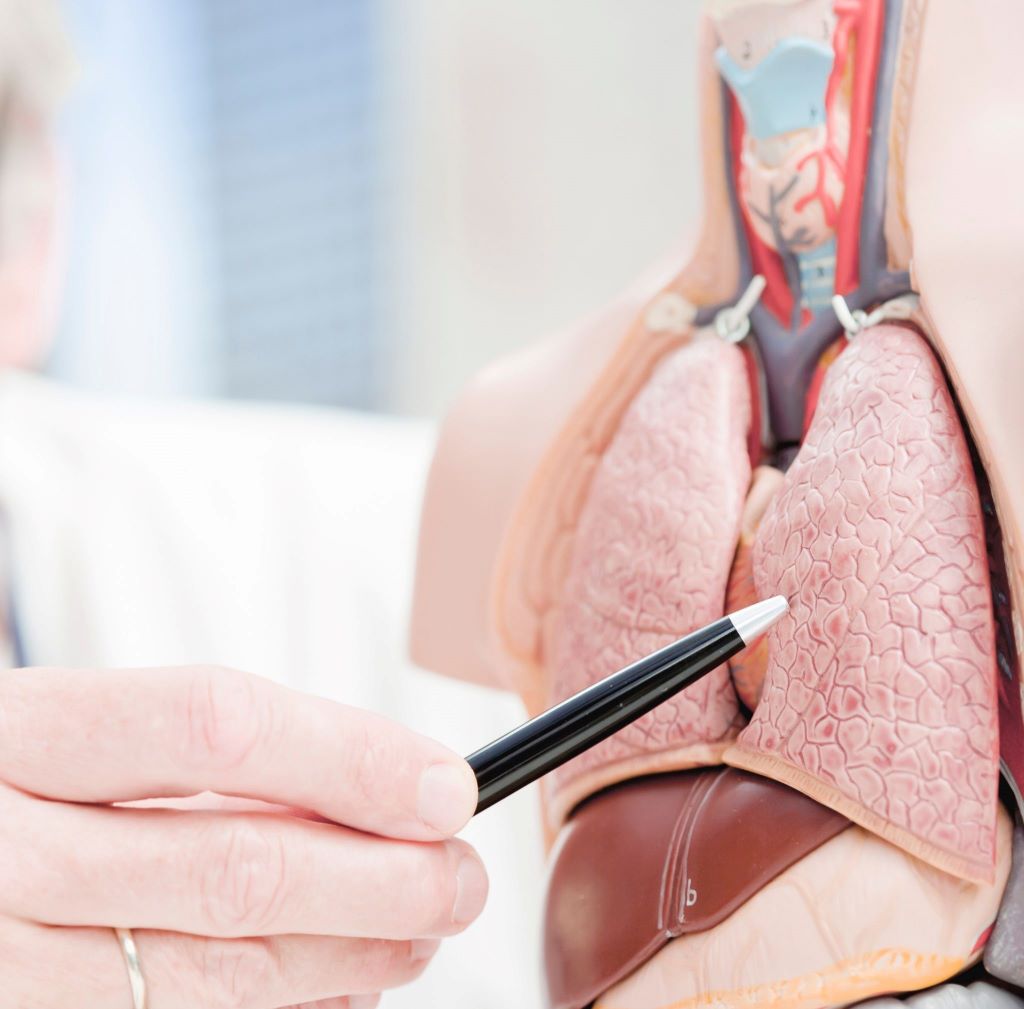
Lung nodules, also known as pulmonary nodules, are small round or oval-shaped growths in the lungs that are usually less than 3 centimeters in diameter. They are often detected incidentally during medical imaging, such as chest X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans, performed for other reasons. Lung nodules can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and their management depends on various factors, including size, shape, growth rate, and the patient’s medical history. The treatment approach aims to determine the cause of the nodules and whether they require further evaluation or intervention.
A lung nodule is a small, abnormal growth or spot found in the lung, typically discovered during a chest X-ray or CT scan. It’s important to understand that the majority of lung nodules – more than 95% of those smaller than 10 millimetres – are benign, meaning they are not cancerous. These non-cancerous nodules can be caused by a variety of factors, including old infections, inflammation, or scar tissue. While a nodule can be a potential sign of early-stage lung cancer, it is not a definitive diagnosis. Further evaluation is always necessary to determine the nature of the nodule.
Lung nodules are quite common and can develop for numerous reasons. The most frequent causes are benign and include:
In some cases, a nodule may represent an early-stage lung cancer, which is why a thorough evaluation by a specialist like me is crucial.
The first step is a comprehensive evaluation. This typically involves a detailed review of your medical history, risk factors (such as smoking history), and the specifics of the nodule on your imaging scan. Depending on the size, shape, and location of the nodule, I may recommend one of the following:
Rest assured, we will discuss all options and decide on the best course of action together.
A biopsy is not always necessary. It is generally recommended if the nodule has suspicious features or if it grows over time. As a specialist in minimally invasive techniques, I prioritise procedures that are both highly accurate and cause minimal discomfort. Common biopsy methods include:
These procedures are performed under sedation or local anaesthesia to ensure your comfort. My team and I are dedicated to making this experience as painless and stress-free as possible.
If a nodule is found to be cancerous, early-stage lung cancer is highly treatable and often curable. As a thoracic surgeon specialising in lung cancer, my primary goal is to offer the most effective and least invasive treatment possible. The gold standard for early-stage lung cancer is surgical removal of the nodule and the surrounding lung tissue. My forte is performing these surgeries using:
These techniques lead to less pain, a shorter hospital stay, and a quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Both are excellent, minimally invasive options.
I will assess your individual case to determine which approach will provide the best possible outcome for you.
Recovery after VATS or robotic surgery is significantly faster than with traditional open surgery. Patients typically experience:
My team will provide you with a detailed recovery plan and support you every step of the way.
When a cancerous lung nodule is completely removed with clear margins (meaning no cancer cells are found at the edge of the removed tissue), the chance of that specific nodule recurring is very low. However, it’s important to attend all follow-up appointments and surveillance scans as recommended. This allows us to monitor your recovery and ensure you remain healthy.
For benign nodules that are surgically removed, the recurrence rate is extremely low.
Whether your nodule is benign or malignant, adopting a healthy lifestyle is always beneficial for your lung health. This includes:
If the nodule is cancerous, these lifestyle changes can also help improve your recovery and overall well-being.
It is completely normal to feel anxious when you learn you have a lung nodule. My approach is to combine the highest standard of medical care with a compassionate and supportive environment. I will take the time to answer all of your questions, explain every step of the process, and ensure you feel confident and informed about your health. We are partners in your care, and my team and I are here to support you both medically and emotionally throughout your journey. Never hesitate to voice your concerns.
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable and often challenging disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a challenging and potentially life-threatening condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. When esophageal...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable adversary that can silently develop within the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube responsible for...
WhatsApp us