What are the Different Stages of Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
+919999461292
MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

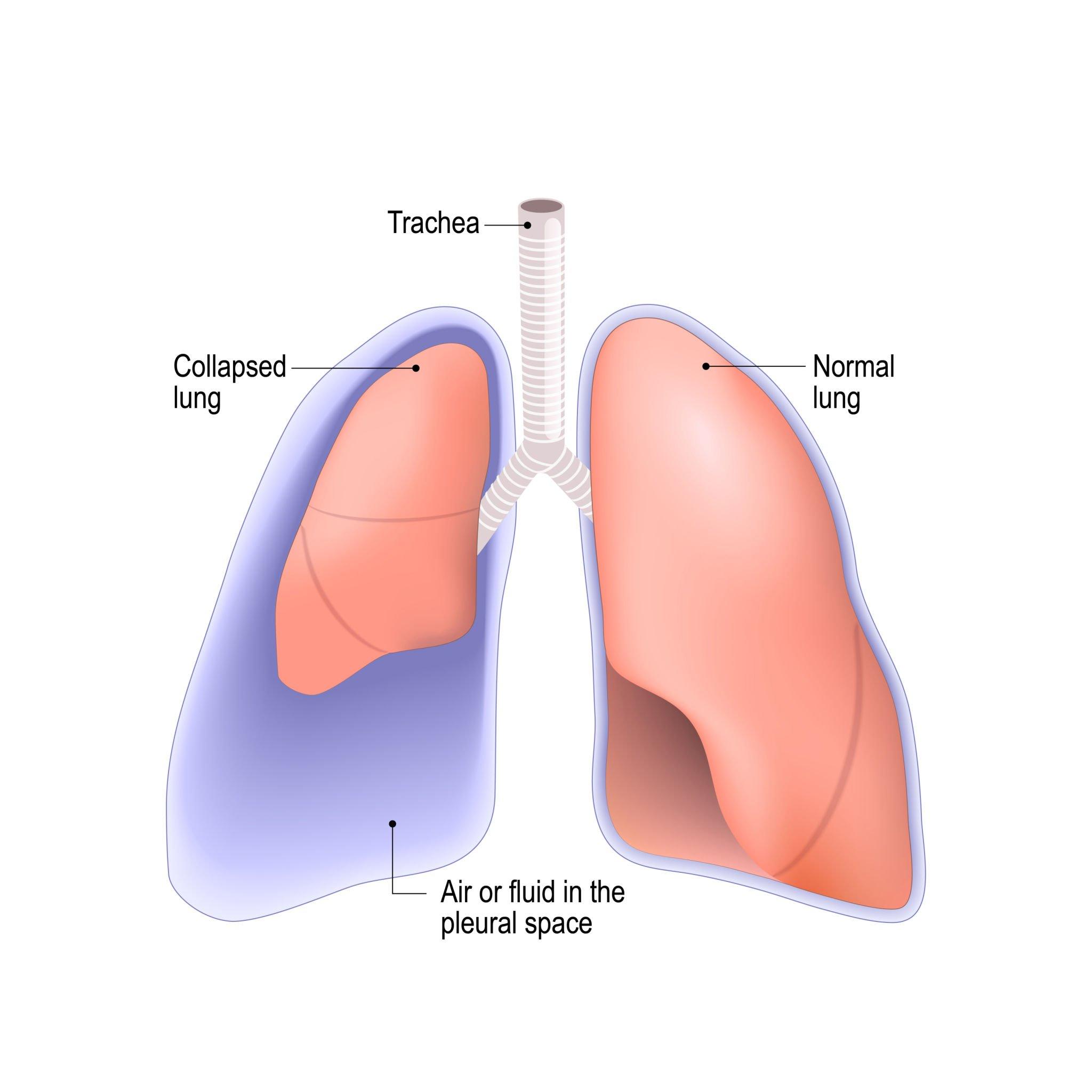
Empyema thoracis is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity, the space between the lungs and the chest wall. This serious complication often results from Tuberculosis or pneumonia but can also develop after trauma. The telltale sign of empyema is a persistent fever, coupled with chest pain, shortness of breath, and a general sense of malaise. These symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation, typically involving chest imaging through X-rays or CT scans, to confirm the presence of fluid accumulation. Laboratory analysis of pleural fluid obtained via thoracentesis, where fluid is drained using a needle, helps in diagnosing infection.
The primary approach to treating empyema thoracis is to drain the infected fluid and administer antibiotics to combat the infection. In cases where fluid is thick or loculated, more invasive procedures, such as Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) or open thoracotomy, may be necessary to thoroughly clear the pleural space. VATS has the advantage of being less invasive, which usually results in quicker recovery and lower risks of complications. Addressing empyema promptly and effectively is crucial to prevent long-term respiratory issues and ensure complete recovery.
Those with concerns or seeking treatment for empyema thoracis should consult with Dr. Mohan Venkatesh Pulle, whose expertise in thoracic surgery provides patients with high-quality, comprehensive care.
See, Empyema is basically accumulation of pus in the chest cavity i.e., the space between your lungs and chest wall. It can cause trouble in breathing and other symptoms.
Well, it can be quite serious if not treated properly. But don’t worry too much – we have very good treatment options these days. Early diagnosis and proper care can lead to full recovery.
Most common symptoms are fever, chest pain, difficulty breathing, and sometimes cough. If you’re experiencing these, especially after a chest infection, it’s important to get checked.
Usually, Empyema develops as a complication of pneumonia or other chest infections. Sometimes it can happen after chest surgery or injury also. Your body’s immune system tries to fight infection, but pus accumulates.
Well, the treatment depends on the severity of the disease. In early empyema, intravenous antibiotics and drainage procedure (Intercostal drain) will suffice. But if these don’t work well, or if infection is very severe, then we might need to do surgery. We’ll decide the best approach for your case.
It varies from patient to patient. Generally, patients stay for 1-2 weeks. But some recover faster, some take a bit longer. We’ll make sure you’re stable before discharge.
See, surgery is required in severe empyema / late empyema. What happens here is, because of a long -standing infection, the layers inside the chest (in medical language we call it – pleura), gets thickened and mechanically restricts the underlying lung expansion. Think it simply as a thick peel over a soft orange pulp. In normal citation, the thickness of this layer is less than a millimeter, but in empyema the thickness increases to a centimeter or more. So, in this surgery we clean all the pus in the chest cavity and also remove this thick peel from the underlying lung surface. It varies from patient to patient. Generally, patients stay for 1-2 weeks. But some recover faster, some take a bit longer. We’ll make sure you’re stable before discharge.
Treatment usually involves antibiotics to fight infection, and drainage of the pus. We might need to insert a chest tube for this. In some cases, we do minimally invasive surgery called VATS to clean out infection.
Recovery time varies, but most patients start feeling better in a few days. Full recovery can take 3-4 weeks. Regular follow-ups and following our instructions will help you recover faster.
Recurrence is not common if treatment is completed properly. But it’s important to finish all medicines and follow-up regularly to prevent any complications.
Main things are – complete your medicines, do breathing exercises we teach you, avoid smoking absolutely, maintain good hygiene and most important high protein diet. Also, attend all follow-up appointments without fail.
Absolutely yes, you can. However, it should be gradual and incremental. We’ll guide you on gradually increasing activity as you recover.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet with good proteins. Include fruits, vegetables, and stay well hydrated. Avoid excessive spicy or oily food. If you’re diabetic, keeping sugar under control is very important.
Most patients return to normal life after full recovery. You might feel tired for some time, but energy levels will improve gradually. We’ll guide you on returning to work and normal activities.
Main things to watch are – increasing breathlessness, fever, or chest pain. If you notice any of these, or any new symptoms, contact us immediately. But don’t worry too much, complications are rare with proper treatment.
Remember, I’m always here to address any concerns. Good communication between doctor and patient is key for successful treatment. Don’t hesitate to ask if you have more questions.
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable and often challenging disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a challenging and potentially life-threatening condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. When esophageal...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable adversary that can silently develop within the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube responsible for...
WhatsApp us