What are the Different Stages of Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
+919999461292
MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

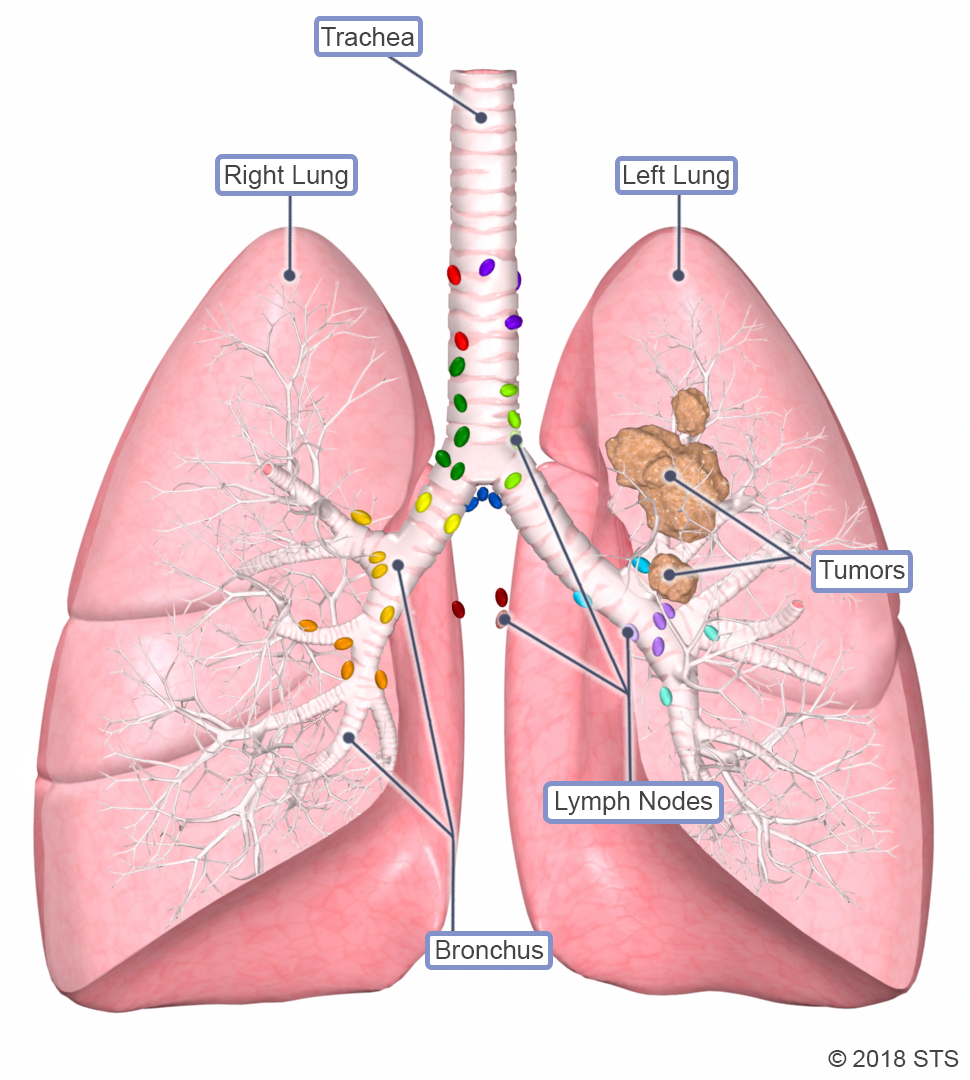
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the lungs, which are essential organs responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during respiration. It is one of the most prevalent and deadly forms of cancer worldwide, affecting both men and women. Lung cancer develops when normal lung cells undergo abnormal changes, leading to uncontrolled growth and the formation of tumors.
There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), which are further categorized based on their specific cell characteristics. NSCLC accounts for about 80% to 85% of all lung cancers, while SCLC makes up approximately 10% to 15%.
See, seriousness depends on cancer stage and type. We’ll do complete staging with PET-CT scan and other tests. Don’t worry too much – nowadays we have many effective treatment options available.
Treatment plan depends on several factors – cancer stage, type, your general health. We might need surgery, or a combination of chemotherapy and radiation. Sometimes we use targeted/immuno therapy also. We’ll discuss best option for your specific case.
Not always immediate. First we need proper staging. Sometimes we give chemotherapy before surgery to shrink tumor.
See, survival rates have improved significantly with modern treatments. Early stage cancers have very good outcomes. But rather than statistics, let’s focus on your specific case and plan the best treatment approach.
Usually 3-4 hours for VATS/robotic procedure. We use minimally invasive techniques – small cuts only. Recovery is much faster compared to traditional surgery.
Yes, there can be side effects like fatigue, nausea. But we have very good medicines to manage these. Remember, not everyone gets all side effects. We’ll monitor you closely and adjust treatment if needed.
After surgery, usually 6-8 weeks for a desk job. Physical work might need 3 months. During chemotherapy, some patients continue working, some need more rest. We’ll plan according to your condition.
We’ll do regular follow-ups to monitor carefully. Risk of recurrence depends on many factors. That’s why completing full treatment and regular check-ups are very important.
Light exercise like walking is actually good during treatment. Helps maintain strength and reduces fatigue. But no heavy exercise until we clear you.
Healthy, protein-rich diet is important. Small, frequent meals if you have poor appetite. Our dietitian will give proper diet plan. Most important – stay well hydrated.
If there’s strong family history, yes, good to get screening done. Especially if family members smoke. We can arrange low-dose CT screening.
First year, every 3 months. Second year, every 6 months. After that, yearly if everything stable. But if any new symptoms develop, contact me immediately.
Most important – no smoking absolutely. Maintain good nutrition, regular exercise as advised, proper rest. Avoid too much stress. We’ll guide you through lifestyle modifications.
Between chemotherapy cycles, if blood counts are good, short trips are okay. But always discuss travel plans with us first. Keep emergency contacts handy.
We have complete support team – counselors, dietitians, physiotherapists. Also can connect you with support groups. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey.
Note: “See, lung cancer treatment is like marathon, not sprint. We’ll be with you at every step. Don’t hesitate to ask any questions – my team and I are always here to help.”
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the lungs, which are essential organs responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during respiration. It is one of the most prevalent and deadly forms of cancer worldwide, affecting both men and women. Lung cancer develops when normal lung cells undergo abnormal changes, leading to uncontrolled growth and the formation of tumors.
There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), which are further categorized based on their specific cell characteristics. NSCLC accounts for about 80% to 85% of all lung cancers, while SCLC makes up approximately 10% to 15%.
Cigarette smoking is the most significant risk factor for developing lung cancer. Approximately 85% of lung cancer cases are directly linked to smoking tobacco, including cigarettes, cigars, and pipes. However, non-smokers can also develop lung cancer, and other risk factors include exposure to secondhand smoke, environmental pollutants (like asbestos, radon, and certain chemicals), family history of lung cancer, and previous radiation therapy to the chest.
Lung cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages, which can make early detection challenging. As the disease progresses, common symptoms include persistent coughing, chest pain, shortness of breath, hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, coughing up blood (hemoptysis), and recurrent respiratory infections like pneumonia or bronchitis.
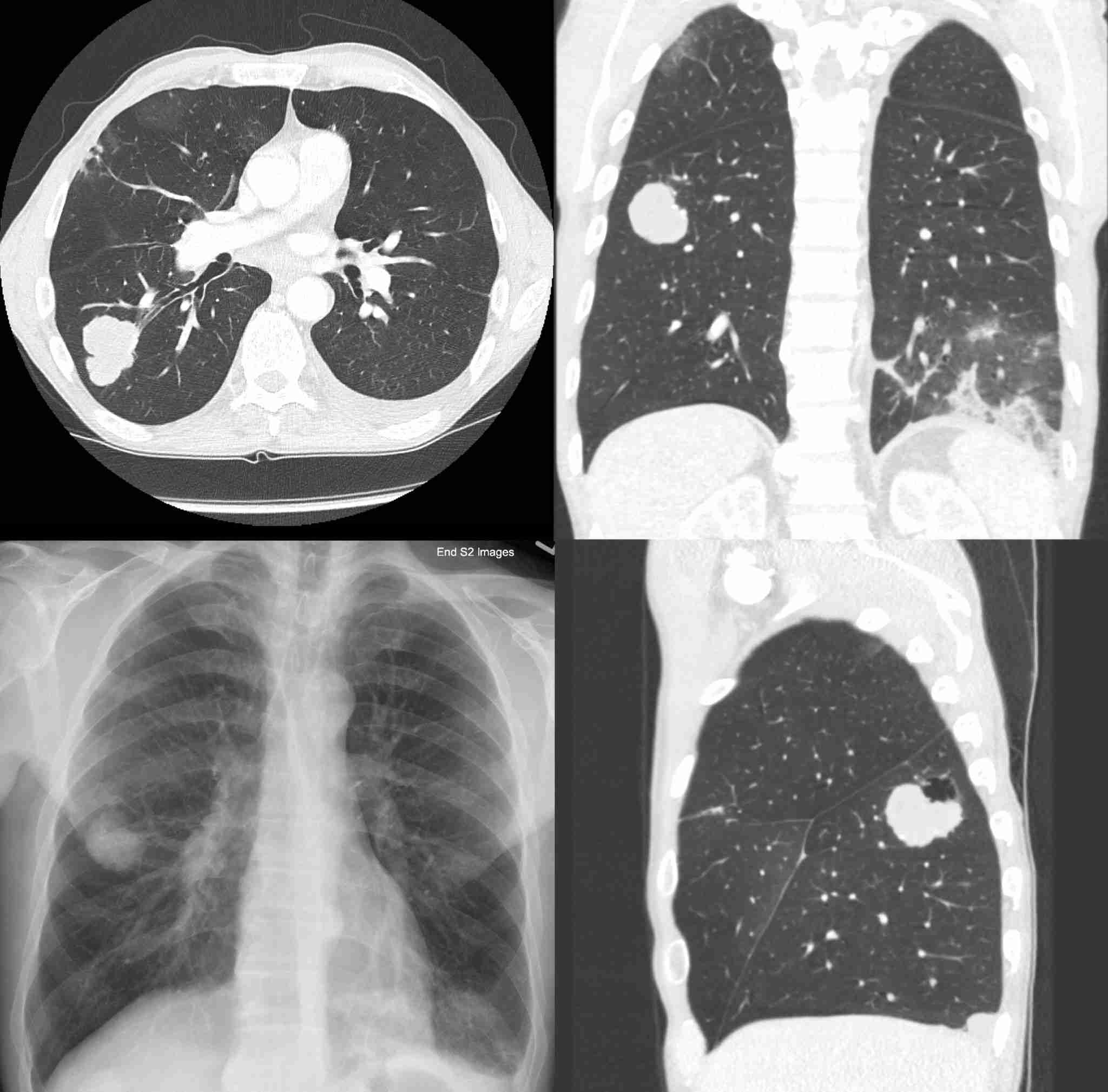
If lung cancer is suspected, the doctor will conduct a thorough evaluation, including a review of the patient’s medical history, risk factors, and symptoms. Diagnostic tests typically include imaging studies like chest X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to identify abnormal growths in the lungs. A biopsy is then performed to collect a tissue sample for examination under a microscope to determine the cancer type and stage.

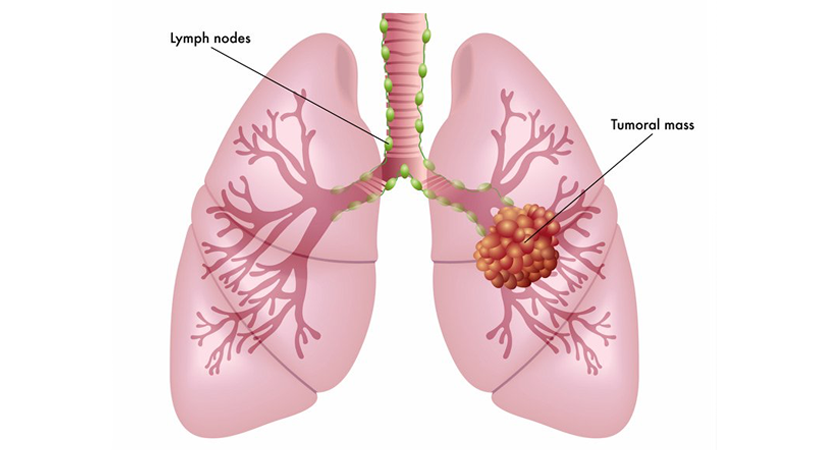
Staging is a crucial step in determining the extent and severity of the cancer. It helps guide treatment decisions and assess the prognosis. The most common staging system for lung cancer is the TNM system, which evaluates the tumor size and extent (T), lymph node involvement (N), and metastasis (M).
The treatment approach for lung cancer depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s overall health. The main treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. For early-stage NSCLC, surgical removal of the tumor may be curative. In advanced cases, a combination of treatments is often used to improve outcomes and manage symptoms.
Lung cancer prognosis varies widely based on the stage at diagnosis and the patient’s response to treatment. Unfortunately, lung cancer is often diagnosed at advanced stages, leading to a lower overall survival rate compared to some other cancers. However, advances in research and treatment have led to improved outcomes for certain cases, particularly when diagnosed early
The best way to prevent lung cancer is to avoid tobacco smoke, both active and passive. For smokers, quitting smoking significantly reduces the risk of developing lung cancer. Reducing exposure to environmental pollutants and known carcinogens is also essential in prevention.
Lung cancer screening is recommended for individuals at high risk, particularly current or former heavy smokers. Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) scans are used for screening, and early detection can lead to more effective treatment and improved survival rates.
A lung cancer diagnosis can be emotionally challenging for both patients and their loved ones. Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can help patients cope with the emotional and practical aspects of the disease. Additionally, palliative care can provide symptom management and improve the quality of life for patients with advanced lung cancer.
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable and often challenging disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a challenging and potentially life-threatening condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. When esophageal...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable adversary that can silently develop within the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube responsible for...
WhatsApp us