What are the Different Stages of Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
+919999461292
MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

The Posterior Mediastinum: Anatomy and Significance
The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity, located between the two pleural sacs that contain the lungs. It is divided into three regions: anterior mediastinum, middle mediastinum, and posterior mediastinum. The posterior mediastinum is the region posterior to the heart and pericardium, and it contains various important structures, including the esophagus, thoracic aorta, thoracic duct, azygos and hemiazygos veins, sympathetic chain, and various lymph nodes. Understanding the anatomy and significance of the posterior mediastinum is crucial for the diagnosis and management of certain conditions.
See, Posterior Mediastinal tumor develops in back portion of chest cavity, between your heart and spine. Think of it like growth in that space. Most of these tumors are neurogenic – means they develop from nerve tissue.
Not always. Actually, many posterior mediastinal tumors are benign, especially in young patients. But we need proper testing to confirm the nature of the tumor. Don’t worry too much – we’ll do a complete evaluation.
These tumors often grow slowly and don’t cause symptoms until they become large. Sometimes they’re found accidentally during chest X-ray for something else. That’s why regular check-ups are important.
We’ll need a CT scan, sometimes an MRI also. These give us detailed pictures of tumor location and size. Sometimes we might need a biopsy to confirm the exact type. All these help us to plan the best treatment.
Usually surgery is the main treatment because these tumors are well-defined and can be removed completely. For most of the tumors, surgery and removal of the total tumor provides a complete cure. We usually perform surgery using minimally invasive surgical techniques such as video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) or Robotic surgery. It means smaller cuts, faster recovery.
Typically 2-3 hours, depending on tumor size and location. We use very advanced techniques now. Most times we can do complete removal through small incisions.
Most patients stay in hospital for 3-5 days after surgery. Complete recovery takes about 4-6 weeks. But you’ll start feeling better much sooner.
Some pain is normal but we manage it well with medicines. Most patients have moderate pain for a few days, then it improves quickly. We’ll ensure you’re comfortable.
Main things to watch – unusual pain, fever, breathing difficulty. But don’t worry too much – complications are quite rare with modern surgical techniques.
Usually can return to a desk job within 2-3 weeks. Physical work might need 4-6 weeks. We’ll assess your recovery and guide accordingly.
Start with gentle walking after a few days. Gradually increase activity. No heavy exercise for 2 months. We’ll give you a proper exercise plan based on your recovery.
Recurrence is quite rare if we remove the tumor completely. But regular follow-up is important to catch any problems early.
Most patients return to normal life without any long-term problems. Regular follow-up helps ensure everything stays fine.
First month weekly, then monthly for 3 months. After that, yearly if everything is stable. But if any problems develop, contact me immediately.
No major restrictions after recovery. Just maintain a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise as advised, and attend follow-ups regularly.
Note: Remember, each patient’s case is a bit different. We’ll make specific plans for your condition. My team and I are always here to support you through the treatment journey.
The Posterior Mediastinum: Anatomy and Significance
The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity, located between the two pleural sacs that contain the lungs. It is divided into three regions: anterior mediastinum, middle mediastinum, and posterior mediastinum. The posterior mediastinum is the region posterior to the heart and pericardium, and it contains various important structures, including the esophagus, thoracic aorta, thoracic duct, azygos and hemiazygos veins, sympathetic chain, and various lymph nodes. Understanding the anatomy and significance of the posterior mediastinum is crucial for the diagnosis and management of certain conditions.

The posterior mediastinum extends from the posterior surface of the heart and pericardium to the anterior border of the thoracic vertebrae (T5 to T12). It is enclosed by the thoracic vertebrae posteriorly, the parietal pleurae laterally, and the diaphragm inferiorly. The structures within the posterior mediastinum are organized into layers from anterior to posterior:
– Anterior Layer: This layer includes the esophagus, thoracic aorta, and azygos vein. The esophagus is a muscular tube that carries food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach. The thoracic aorta is the large artery that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. The azygos vein and its counterpart, the hemiazygos vein, are important vessels that drain blood from the posterior chest wall.
– Middle Layer: The middle layer consists of the sympathetic chain, which is part of the autonomic nervous system responsible for involuntary functions in the body.
– Posterior Layer: This layer includes structures such as the thoracic duct, lymph nodes, and fat tissues.
The posterior mediastinum contains critical structures that play essential roles in the functioning of the cardiovascular and digestive systems, as well as the nervous and lymphatic systems. Understanding the anatomy and function of these structures is crucial for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
Several medical conditions can affect the structures within the posterior mediastinum, leading to various symptoms and health issues. Some of the notable disorders and conditions include:
– Esophageal Disorders: Conditions affecting the esophagus, such as esophageal cancer, esophageal strictures (narrowing), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), can lead to difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and other gastrointestinal symptoms.
– Aortic Aneurysm: An abnormal bulging of the aortic wall in the thoracic region can lead to an aortic aneurysm. If left untreated, it can be life-threatening due to the risk of rupture and internal bleeding.
– Neurogenic Tumors: Tumors that originate from the sympathetic chain or other neural structures in the middle mediastinum can cause various neurological symptoms depending on their location and size.
– Thoracic Duct Disorders: The thoracic duct is the primary lymphatic vessel responsible for draining lymphatic fluid from the lower body and left upper body. Disorders such as thoracic duct obstruction can lead to lymphedema and other lymphatic-related issues.
– Lymph Node Abnormalities: Enlarged or abnormal lymph nodes in the posterior mediastinum can be indicative of infections, inflammation, or cancer, and may require further evaluation and treatment.
– Aortic Dissection: A life-threatening condition in which there is a tear in the inner lining of the aorta, causing blood to flow between the layers of the vessel wall.
– Trauma: Injuries to the thoracic region, such as fractures of the thoracic vertebrae, can affect the structures in the posterior mediastinum.
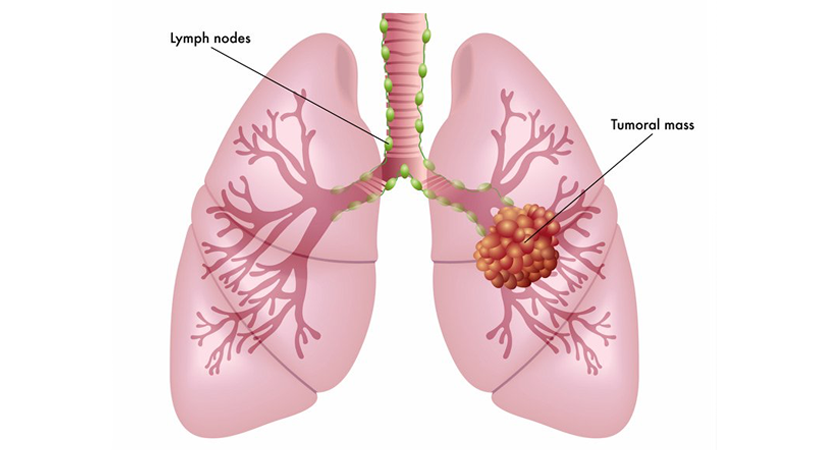
When evaluating patients with symptoms or conditions related to the posterior mediastinum, several diagnostic approaches may be employed:
– Imaging Studies: Chest X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) scans can help visualize the structures in the posterior mediastinum and detect any abnormalities.
– Endoscopy: Esophagoscopy can be used to directly visualize the esophagus and identify any lesions or strictures.
– Biopsy: If abnormal growths or lymph nodes are detected, a biopsy may be performed to obtain tissue samples for examination under a microscope to determine the nature of the condition.
– Blood Tests: Certain blood tests can help evaluate the overall health of the patient and identify any abnormalities related to specific conditions, such as aortic aneurysm or infection.
The treatment and management of conditions affecting the posterior mediastinum depend on the specific disorder or condition diagnosed. Treatment options may include:
– Surgery: Surgical interventions may be necessary for conditions such as esophageal cancer, aortic aneurysm repair, or removal of tumors.
– Radiation Therapy: For certain cancers, radiation therapy may be used to target and destroy cancerous cells.
– Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be employed in conjunction with other treatments for cancers that have spread beyond the mediastinum.
– Symptom Management: In cases where a cure is not possible, the focus may be on symptom management and improving the patient’s quality of life.
– Lymphedema Management: For disorders affecting the lymphatic system, such as thoracic duct obstruction, specialized management techniques may be used to alleviate symptoms.
Research in the field of thoracic medicine continues to advance our understanding of the posterior mediastinum and its disorders. New diagnostic techniques, treatments, and surgical approaches are constantly being developed to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable and often challenging disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a challenging and potentially life-threatening condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. When esophageal...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable adversary that can silently develop within the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube responsible for...
WhatsApp us