What are the Different Stages of Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
+919999461292
MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

MBBS | DNB (General Surgery, Gold Medalist) | DNB (Thoracic Surgery, Gold Medalist)
Thoracic & Lung Transplant Surgeon | Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram

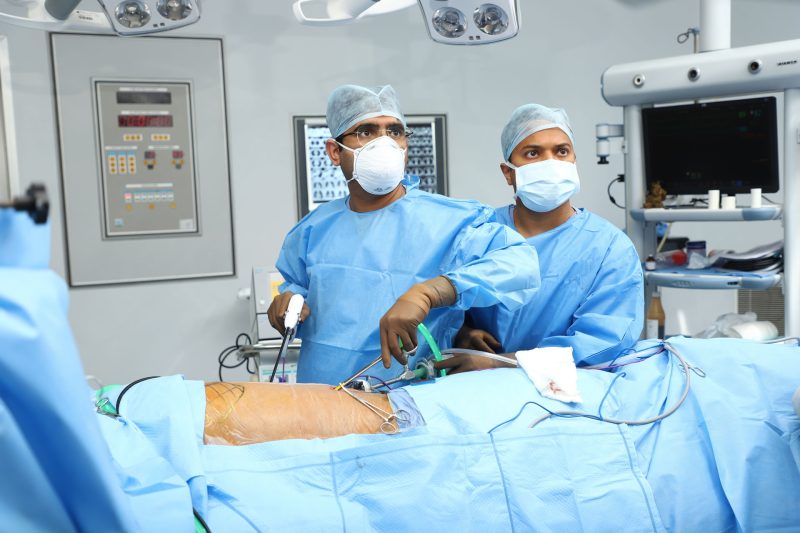
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) is a minimally invasive surgical technique used in various lung treatments. It involves the use of a video camera and specialized instruments to perform surgery through small incisions in the chest. VATS has gained popularity over the years as it offers several benefits over traditional open surgeries, including reduced trauma, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery. This article explores the process and advantages of VATS surgery in lung treatments
The VATS procedure involves several key steps:
Esophageal cancer is a formidable disease that affects the esophagus, the hollow tube that carries food and liquids...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable and often challenging disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a challenging and potentially life-threatening condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. When esophageal...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries...
Esophageal cancer is a formidable adversary that can silently develop within the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the...
Esophageal cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube responsible for...
WhatsApp us